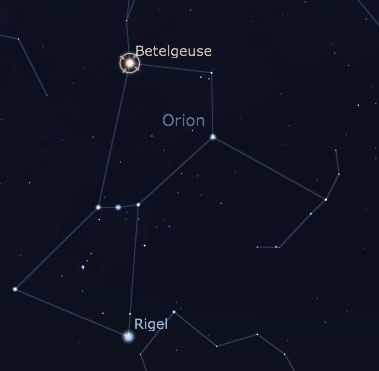
Betelgeuse:
Alpha Orionis is the distinctive red super giant Betelgeuse. Despite its “alpha” designation, and it’s rank as the ninth brightest star in the sky, it is not the brightest star in Orion … that designation goes to Rigel. Betelgeuse is a fascinating star, however, it is so large that its unstable and fluctuates in size (between 300 and 400 times the diameter of the Sun) and brightness (between magnitude 1.3 and 0.0). As a point of reference … if Betelgeuse were at the center of the Solar System, its surface would extend past the asteroid belt.
Betelgeuse is foremost known as Orion’s brightest shoulder … but it is also part of the Winter Triangle also known as the Great Southern Triangle. This equilateral triangle is made up of Betelgeuse (Orion), Sirius (Canis Major) and Procyon (Canis Minor).
Final Note: The star’s unusual name inspired the title of the 1988 film Beetlejuice, staring Michael Keaton. Script writer Michael McDowell was impressed by how many people made the connection. I guess we are indeed smart … so heed the warning, never say “Beetlejuice” three times in a row, if you know what’s good for you.
.
Betelgeuse Overview:
- Constellation Orion
- Alpha (α) 5h55m, +07°24′
- Type Giant star
- Magnitude 0.0 – 1.3
- Luminosity 85,000 Suns
- Spectral Type M1.5 lab
- Distance 570 light years
Orion Constellation … The Hunter
One of the best known constellations in the nights sky, Orion straddles the celestial equator, so that it’s visible anywhere on Earth. Representing the hunter from Greek and Roman myth, bright stars mark the shoulders (Betelgeuse & Bellatrix) and knees (Rigel & Saiph), while fainter ones trace the position of the hunter’s head, his raised shield and his club. The centerpiece of the constellation is a distinctive chain of three fairly bright stars marking the hunter’s belt. Fainter stars/nebulas make up the short chain which includes the Great Orion Nebula M42, that shows the location of his sword.
Orion is the center of a complex scene involving many of the surrounding constellations, Canis Minor and Major, directly behind him represent his hunting dogs. His foe Taurus the attacking bull that he is attempting to fend off. Lastly there is Lepus the hare that is cowering at his feet.
Astronomy 101
